Cloud Computing
Introducing Bash
Bash (Bourne Again Shell) is the standard scripting language for managing Linux machines.
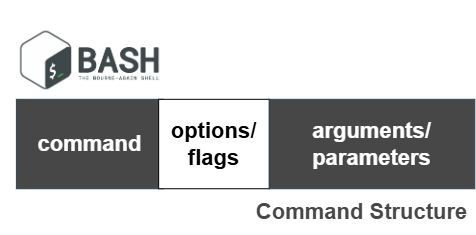
Command is the action to be performed, while options equally know as flags define the behaviour of the command. Options are optional and some options require additional values known as arguments or parameters.
command [-flag(s)] [-option(s) [value]] [argument(s)]
Getting Help
Bash has an in-built manual [man] that be referenced to learn more about the commands on the go. Eg. running the command man ls will show the details of the ls command.
Bash Wildcards
This comes handy when you want to match multiple files or strings. Three common wildcards include:
- Asterisk()
ls *.txtcommand will list all the text files in current directory.- ls *.jpg *.png match multiple file extensions
- ls *.jp*g can be used to match both jpg and jpeg.
- Question Mark (?)
ls searchstring?.txtwill match with the filenames as well. - Square brackets ([]) matches character ranges.
- Eg.
ls [a-z]*matches files in current directory whose names start with lowercase letters. ls [a-zA-Z]*matches lower and uppercase letters.
- Eg.
Bash I/O Operators
You can redirect input from a source other than the keyboard, redirect output to a source other than the screen with Bash commands.
ls >notes.txt will list the contents of a folder in a text file rather than display it on the screen.ls -l >>notes.txt will append the properties of the items to the text file.
The < operator is used to get input from other sources than the keyboard eg. wc < notes.txt. You can even save the results in a new file. wc < notes.txt > wordcount.txt.
Bash Pipes
Piping in bash redirects output from one command to another. command1 | command2. Let's say you have a text file called sample.txt with the following content: apple, banana, cherry, date, fig. And you want to filter out the lines containing the letter "a" and sort the remaining alphabetically.
- cat sample.txt | grep 'a' | sort
End Unwanted Process
You can kill unwanted processes with the kill command. Run ps -ef to list active processes on your machine. The command gives a detailed list of all the processes running o your system. You can use grep command to filter your result with a search string.
- Eg.
ps -ef | grep phpHere we piped two commands together, to get all running processes and list the ones that contain python in their name. Then we runkill -9 [process_id]to instantly end the process.
Delete files and folders
rm filename.extdelete a filerm foldernamedelete an empty folderrm -r foldernamedelete a folder along with its contents
Combine the contents of a file into a new file with
cat file1 file2 > newfile
Finally, run command with elevated privilege with sudo.
sudo apt install htop
- Hits: 207

Ireland | Bobby Abuchi