Take Your Data Skills to Next Level with Microsoft Fabric 📈📊
If you have not come across it, let me introduce you to Microsoft Fabric, a unified environment that enhances the way we work with data. Fabric is not a specific product or platform, but more of a concept that refers to the integrated and unified capabilities of Microsoft Cloud services particularly in data and #analytics space.
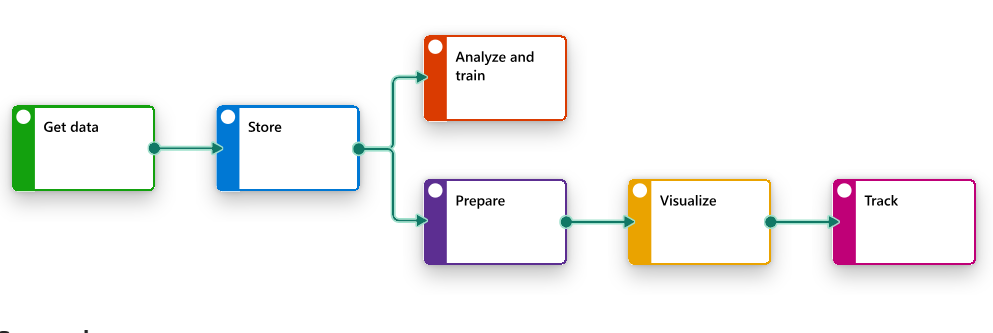
There are up to eight different services including; Data Factory, Synapse Data Warehouse and Power BI working together seamlessly to provide a comprehensive data platform.

In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, some organisations face challenges in managing complex data workflows, integrating multiple services and providing real-time insights. The struggles with data silos, manual processes and delayed decision making are becoming part of the job but should not be the case.
How about a system that integrates multiple data related services, streamlines data workflows and enable real-time insights thereby bringing together data movement, processing, ingestion, transformation, even event routing and report building into a single user-friendly environment?
This is where Microsoft Fabric comes in. This solution integrates data related services like Data Factory, Synapse Data Warehouse and Power BI so with this we have in one place:
- Data Factory for easy data movement and processing
- Synapse Data Warehouse for advanced analytics
- Power BI for data visualisation
Other services in the Fabric include Synapse Data Science, Real-Time Intelligence, Synapse Data Engineering, and Data Activator. Hopefully, I will a share project that utilised all these services so we can see how everything works together for good, in data management and analytics.
Adopting the Fabric approach can significantly reduce data workflow complexity, increase data processing speed, improve report building and visualisation capabilities, enhance collaboration and decision-making with real-time insights.
And your team can easily learn and adapt with minimal training and support. Microsoft Learn offers extensive documentation, tutorials and training resources. Intuitive interface, drag-and-drop features of the services make them easy to use. Data Factory and Synapse Analytics offer predesigned templates for streamlined setup and easy configuration.
Synapse Analytics Predesigned Template
- Hits: 165

Ireland | Bobby Abuchi